| Klimawandel - Climate Change |
 |
Klimakonferenz-COP28 Dubai 2023 |
 |
NGOs über COP28 |
 |
COP: Weitere Informationen |
 |
Klimawandel Weitere Informationen |
|
|
| UNO Klimakonferenz-COP28 Dubai (V.A.E) 2023 |
 |
| Die Weltklimakonferenz COP28 fand vom 30. November 2023 bis zum 13. Dezember 2023 in Dubai (Vereinigte Arabische Emirate) statt.
|
| Die Weltklimakonferenz COP (UN Framework Convention on Climate Change Conference of the Parties) ist die grösste zwischenstaatliche Konferenz für Klimafragen.
|
|
An der 28. UNO-Klimakonferenz (COP28) in Dubai (Vereinigte Arabische Emirate) ist ein wichtiges Thema, wie sich das Ziel, die Erderwärmung auf 1,5 Grad zu begrenzen, in Reichweite halten lässt. Im Zentrum der diesjährigen COP steht der sogenannte «Global Stocktake», in dessen Rahmen die Staaten zum ersten Mal gemeinsam Bilanz über die Fortschritte ziehen, die unter dem Pariser Übereinkommen erreicht wurden.
| Weltklimakonferenz: "Insgesamt starkes Signal" aus Dubai |
 |
Die Umwelt- und Entwicklungsorganisation Germanwatch zieht ein überwiegend positives Fazit der Weltklimakonferenz in Dubai. Der Abschlusstext enthalte zwar Schwächen, sende aber auch in zentralen Bereichen starke Botschaften. "Die COP28 sendet insgesamt ein starkes Signal an die Welt. Erstmals fordert eine Weltklimakonferenz alle Staaten auf, die Wende weg von Kohle, Öl und Gas zu organisieren. Das ist ein wichtiger Schritt", sagt Christoph Bals, Politischer Geschäftsführer von Germanwatch. "Historisch ist dieser Schritt allerdings nur, wenn in den nächsten Jahren tatsächlich weltweit ein massives Herunterfahren von Kohle, Öl und Gas erfolgt."
Entsprechende Aktivitäten für die Abkehr von fossilen Energien sollen laut Beschluss in diesem entscheidenden Jahrzehnt, also bis 2030, beschleunigt werden. Dies wird untermauert durch die Aufforderung, zur Umsetzung der sehr ambitionierten globalen Ziele für Erneuerbare Energien und Energieeffizienz beizutragen. Diese Ziele sehen eine Verdreifachung der heute installierten Erneuerbaren Energien und eine Verdopplung der Energieeffizienz bis 2030 vor. Um dieses Ziel zu Hause umzusetzen, müssen die EU-Mitgliedsstaaten - Deutschland eingeschlossen - allerdings noch ihre Hausaufgaben machen. Stand heute ist die EU weit weg von einem Kurs, ihr neues Erneuerbaren-Energien-Ziel für 2030 von 42,5 bis 45 Prozent Anteil am Energiemix zu erreichen. Bals: "Auch die EU ist jetzt in der Pflicht, alles dafür zu tun, dass die globalen Treibhausgas-Emissionen tatsächlich bis 2030 um 43 Prozent gegenüber 2019 sinken, so wie es die Wissenschaft für einen 1,5 Grad-Pfad fordert. Nicht nur die kleinen Inselstaaten haben Zweifel, dass alle Staaten dabei an einem Strang ziehen. Die Akzeptanz von Gas als Brückentechnologie im Beschlusstext kann grosse Schlupflöcher öffnen."
| COP28 Agreement Signals "Beginning of the End" of the Fossil Fuel Era |
 |
The United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) closed today with an agreement that signals the "beginning of the end" of the fossil fuel era by laying the ground for a swift, just and equitable transition, underpinned by deep emissions cuts and scaled-up finance.
In a demonstration of global solidarity, negotiators from nearly 200 Parties came together in Dubai with a decision on the world’s first ‘global stocktake’ to ratchet up climate action before the end of the decade - with the overarching aim to keep the global temperature limit of 1.5°C within reach.
"Whilst we didn’t turn the page on the fossil fuel era in Dubai, this outcome is the beginning of the end," said UN Climate Change Executive Secretary Simon Stiell in his closing speech. "Now all governments and businesses need to turn these pledges into real-economy outcomes, without delay."
The global stocktake is considered the central outcome of COP28 - as it contains every element that was under negotiation and can now be used by countries to develop stronger climate action plans due by 2025.
The stocktake recognizes the science that indicates global greenhouse gas emissions need to be cut 43% by 2030, compared to 2019 levels, to limit global warming to 1.5°C. But it notes Parties are off track when it comes to meeting their Paris Agreement goals.
The stocktake calls on Parties to take actions towards achieving, at a global scale, a tripling of renewable energy capacity and doubling energy efficiency improvements by 2030. The list also includes accelerating efforts towards the phase-down of unabated coal power, phasing out inefficient fossil fuel subsidies, and other measures that drive the transition away from fossil fuels in energy systems, in a just, orderly and equitable manner, with developed countries continuing to take the lead.
In the short-term, Parties are encouraged to come forward with ambitious, economy-wide emission reduction targets, covering all greenhouse gases, sectors and categories and aligned with the 1.5°C limit in their next round of climate action plans (known as nationally determined contributions) by 2025.
Helping countries strengthen resilience to the effects of climate change
The two-week-long conference got underway with the World Climate Action Summit, which brought together 154 Heads of States and Government. Parties reached a historic agreement on the operationalization of the loss and damage fund and funding arrangements - the first time a substantive decision was adopted on the first day of the conference. Commitments to the fund started coming in moments after the decision was gaveled, totaling more than USD 700 million to date.
There was more progress on the loss and damage agenda with an agreement also reached that the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction and the UN Office for Project Services will host the secretariat of the Santiago Network for Loss and Damage. This platform will catalyze technical assistance to developing countries that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change.
Parties agreed on targets for the Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA) and its framework, which identify where the world needs to get to in order to be resilient to the impacts of a changing climate and to assess countries’ efforts. The GGA framework reflects a global consensus on adaptation targets and the need for finance, technology and capacity-building support to achieve them.
Increasing climate finance
Climate finance took center stage at the conference, with Stiell repeatedly calling it the "great enabler of climate action."
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) received a boost to its second replenishment with six countries pledging new funding at COP28 with total pledges now standing at a record USD 12.8 billion from 31 countries, with further contributions expected.
Eight donor governments announced new commitments to the Least Developed Countries Fund and Special Climate Change Fund totaling more than USD 174 million to date, while new pledges, totaling nearly USD 188 million so far, were made to the Adaptation Fund at COP28.
However as highlighted in the global stocktake, these financial pledges are far short of the trillions eventually needed to support developing countries with clean energy transitions, implementing their national climate plans and adaptation efforts.
In order to deliver such funding, the global stocktake underscores the importance of reforming the multilateral financial architecture, and accelerating the ongoing establishment of new and innovative sources of finance.
At COP28, discussions continued on setting a ‘new collective quantified goal on climate finance’ in 2024, taking into account the needs and priorities of developing countries. The new goal, which will start from a baseline of USD 100 billion per year, will be a building block for the design and subsequent implementation of national climate plans that need to be delivered by 2025.
Looking ahead to the transitions to decarbonized economies and societies that lie ahead, there was agreement that the mitigation work programme, which was launched at COP27 last year, will continue until 2030, with at least two global dialogues held each year.
Event participation and inclusivity
World leaders at COP28 were joined by civil society, business, Indigenous Peoples, youth, philanthropy, and international organizations in a spirit of shared determination to close the gaps to 2030. Some 85,000 participants attended COP28 to share ideas, solutions, and build partnerships and coalitions.
The decisions taken here today also reemphasize the critical importance of empowering all stakeholders to engage in climate action; in particular through the action plan on Action for Climate Empowerment and the Gender Action Plan.
Strengthening collaboration between governments and key stakeholders
In parallel with the formal negotiations, the Global Climate Action space at COP28 provided a platform for governments, businesses and civil society to collaborate and showcase their real-world climate solutions.
The High-Level Champions, under the Marrakech Partnership for Global Climate Action, launched their implementation roadmap of 2030 Climate Solutions. These are a set of solutions, with insights from a wide range of non-Party stakeholders on effective measures that need to be scaled up and replicated to halve global emissions, address adaptation gaps and increase resilience by 2030.
The conference also saw several announcements to boost the resilience of food and public health systems, and to reduce emissions related to agriculture and methane.
Looking ahead
The negotiations on the ‘enhanced transparency framework’ at COP28 laid the ground for a new era of implementing the Paris Agreement. UN Climate Change is developing the transparency reporting and review tools for use by Parties, which were showcased and tested at COP28. The final versions of the reporting tools should be made available to Parties by June 2024.
COP28 also saw Parties agree to Azerbaijan as host of COP29 from 11-22 November 2024, and Brazil as COP30 host from 10-21 November 2025.
The next two years will be critical. At COP29, governments must establish a new climate finance goal, reflecting the scale and urgency of the climate challenge. And at COP30, they must come prepared with new nationally determined contributions that are economy-wide, cover all greenhouse gases and are fully aligned with the 1.5°C temperature limit.
"We must get on with the job of putting the Paris Agreement fully to work," said Stiell. "In early 2025, countries must deliver new nationally determined contributions. Every single commitment - on finance, adaptation, and mitigation - must bring us in line with a 1.5-degree world."
"My final message is to ordinary people everywhere raising their voices for change," Stiell added. "Every one of you is making a real difference. In the crucial coming years your voices and determination will be more important than ever. I urge you never to relent. We are still in this race. We will be with you every single step of the way."
"The world needed to find a new way. By following our North Star, we have found that path," said COP28 President, Dr. Sultan Al Jaber during his closing speech. "We have worked very hard to secure a better future for our people and our planet. We should be proud of our historic achievement."
| Source: Text UNFCCC, 13 December 2023 |
 |
| Klimakonferenz-COP10
Buenos Aires 2004 |
| COP10:
Ein Sachgeschäft - Brandrodungen verschlimmern Treibhauseffekt |
 |
Die
Zerstörung des brasilianischen Regenwaldes durch Brandrodungen
ist hauptverantwortlich für die schädlichen Gasemissionen des
südamerikanischen Landes, die den so genannten Treibhauseffekt
verursachen. Das geht aus einer Regierungsstudie aus den Jahren 1990 bis
1994 hervor, die in Brasilien erstmals veröffentlicht wurde. Die Studie
wird auch bei der UNO-Klimakonferenz COP10 vorgestellt.
Nach
der in Brasilia veröffentlichten Studie war das grösste Land
Lateinamerikas zwischen 1990 und 1994 für drei Prozent aller weltweiten
Treibhaus-Gasemissionen verantwortlich. Als überraschend werteten
Experten die Tatsache, dass die Brandrodungen zur Vorbereitung von Anbauflächen
im Urwald 1994 für drei Viertel aller Treibhausgasemissionen in Brasilien
sorgten. Die Verbrennung fossiler Brennstoffe hatte nur einen Anteil von
23 Prozent.
Der
brasilianische Ausstoss von Kohlendioxid (CO2), jenes Gases, das für
den Treibhauseffekt und die globale Temperaturerhöhung hauptverantwortlich
ist, erhöhte sich laut der Studie allein zwischen 1990 und 1994 um
fünf Prozent auf 1,03 Milliarden Tonnen.
Brasiliens
Regierung versicherte, dass sie tue alles, um die Zerstörung des Regenwaldes
zu bremsen. Dazu müssten vor allem die illegalen Aktivitäten
bekämpft werden, sagte sie.
| vor 12 Jahren bis 17 Jahren |
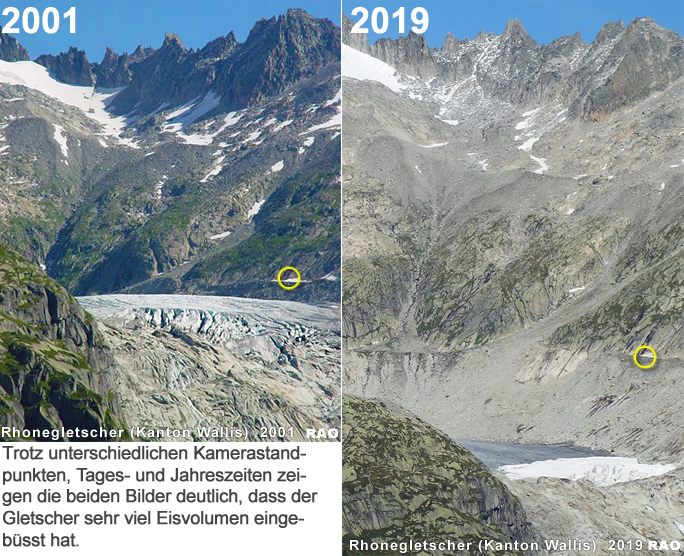
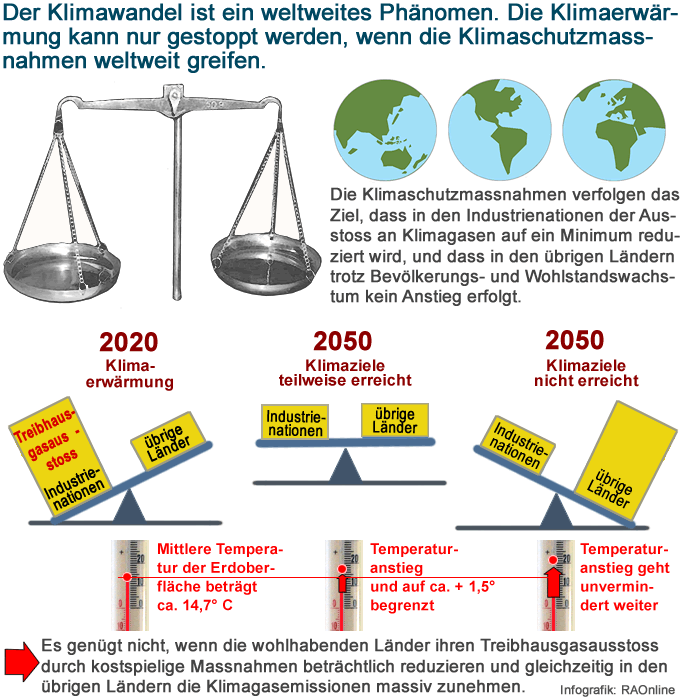
Bereits zu Beginn des neuen Jahrtausends ud frpüher warnten die Klimawissenschaftler eindringlich vor den Folgen des Klimawandels. Ende 2019 wissen wir, ihre Voraussagen sind mehrheitlich nachprüfbar eingetroffen. Die Warnrufe der Wissenschaft sind nicht verstummt. Im Gegenteil! Seit 20 Jahren wird das Konsum- und Freizeitverhalten derart "gepuscht", wie wenn die Folgen des Klimawandels weiterhin Fiktion bleiben würden.
| Schlagzeilen 2003 - 2007 |
 |
| Vorbote
der Klimazukunft |
2003 |
|
| Unbeständigkeit nimmt zu |
2003 |
|
| Es
braucht eine langfristige Politik |
2004 |
|
|
| Klimakrise näher denn je |
2004 |
|
| Klimaänderung so rasant wie noch nie |
2005 |
|
| Es wird heiss in Europa |
2005 |
|
|
|