 |
| Earthquakes in Nepal |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| Earthquakes - Richter and Mercalli Scales |
| Earthquakes: Richter Scale |
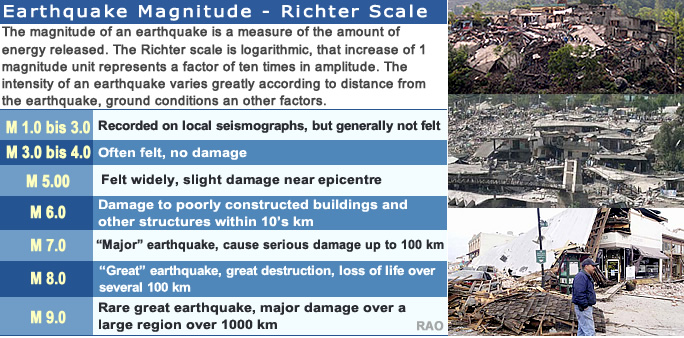 |
| MODIFIED MERCALLI INTENSITY SCALE |
| ESTIMATED INTENSITY | PERCEIVED SHAKING | POTENTIAL DAMAGE |
| I II-III IV V VI VII VIII IX X |
Not Felt Weak Light Moderate Strong Very Strong Severe Violent Extreme |
None None None Very Light Light Moderate Moderate/Heavy Heavy Very Heavy |
 |
| I | People do not feel any earth movement. |
| II | Felt by persons at rest, on upper floors of tall buildings |
| III | Felt by people indoors.
Hanging objects swing back and forth.
May not be recognized as an earthquake. |
| IV | Hanging objects swing.Vibration may seem like the passing of heavy trucks or a jolt, like a heavy ball striking the walls.
Parked vehicles may rock noticeably. Windows, dishes, doors may rattle and glasses clink. In the upper range of IV, walls of wood frame buildings may creak. |
| V | Almost everyone feels movement whether inside or outdoors.
Sleeping people are awakened. Liquids in containers are disturbed; some are spilled.Small unstable objects are displaced or overturned. Doors swing, close, or open.Shutters, pictures on the wall move. |
| VI | Felt by all; some are frightened and take cover.
People have difficulty walking due to motion. Objects fall from shelves and dishes, glassware and ceramics may be broken. Pictures fall off walls. Furniture moves or is overturned.Weak plaster and masonry cracked. Damage slight in poorly constructed buildings. Trees, bushes shaken visibly or are heard rustling. |
| VII | People have difficulty standing. Drivers on the road feel their cars shaking. Furniture may be overturned and broken. Loose bricks fall from buildings and masonry walls and cracks in plaster and masonry may appear. Weak chimneys may break at the roofline. Damage is slight to moderate in well-built structures; considerable in poorly constructed buildings and facilities. |
| VIII | Drivers have trouble steering.
Tall structures such as towers, monuments and chimneys may twist and fall. Wood frame houses that are not bolted to their foundations may shift and sustain serious damage. Damage is slight to moderate in well-constructed buildings, considerable in poorly constructed buildings. Branches are broken and fall from trees. Changes occur in flow or temperature of springs and wells. Cracks appear in wet ground and on steep slopes. |
| IX | Masonry structures and poorly constructed buildings suffer serious damage or collapse.
Frame structures, if not bolted, shift off foundations. Serious damage to reservoirs.Underground pipes broken.
|
| X | Most masonry and frame structures destroyed along with their foundations.
Some well-built wooden structures and bridges are destroyed.Serious damage to dams, dikes, and embankments. Large landslides occur. Water thrown on the banks of canals, rivers and lakes. Sand and mud shift horizontally on beaches and flat land. Rails bent. |
| Contributed by United States Geological Survey (USGS), 2009 |
|
Nepal |
| Links |
| External link |
|
Nepal |
|
|
|
|